|
|
|
The Maine Medicaid
Study also found that patients diagnosed with SMI not only experienced higher
rates of specific illnesses, but also experienced higher rates of combined
(multiple) and serious diseases.
|
|
|
|
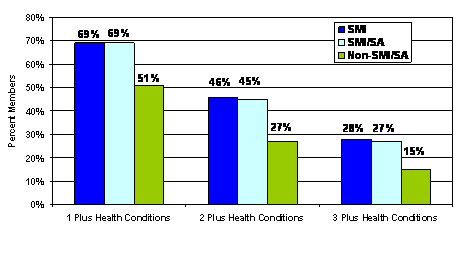
This slide compares
the 2004 prevalence of medical conditions among the Seriously Mentally Ill
(SMI with and without substance abuse) vs. non-SMI [Medicaid recipients
without mental health conditions or substance abuse]:
|
|
|
|
SMI non-SMI
|
|
1 plus conditions 69% 51%
|
|
2 plus conditions 46% 27%
|
|
3 or more conditions 28% 15%
|
|
|
|
[Source of data:
Freeman, E. and Yoe, J.T., as referenced above.]
|
|
|
|
Key Point:
Among recipients of Medicaid, SMI is associated with higher rates of
physical (somatic) medical disease.
|